
If you’ve ever dreamed about mounting that “Great Gatsby” musical, or writing that sci-fi adaptation based on Gatsby but they’re all androids, there’s some good news: as of January 1, 2021, F. Scott Fitzgerald’s classic novel finally entered the public domain. (Read a public domain copy here.) Creatives can now do what they want with the work: reprint or adapt it any way they like, without having to negotiate the rights.
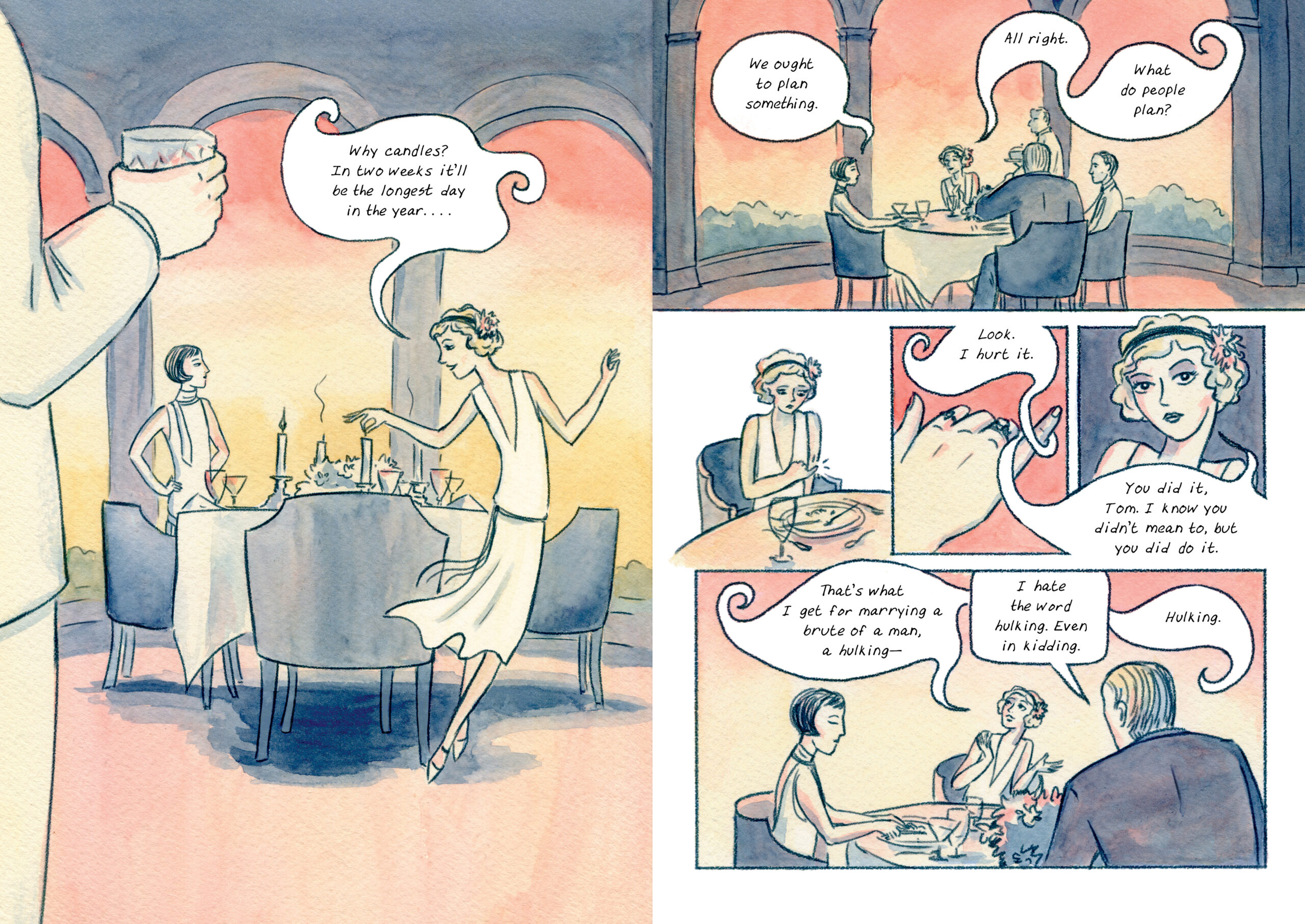
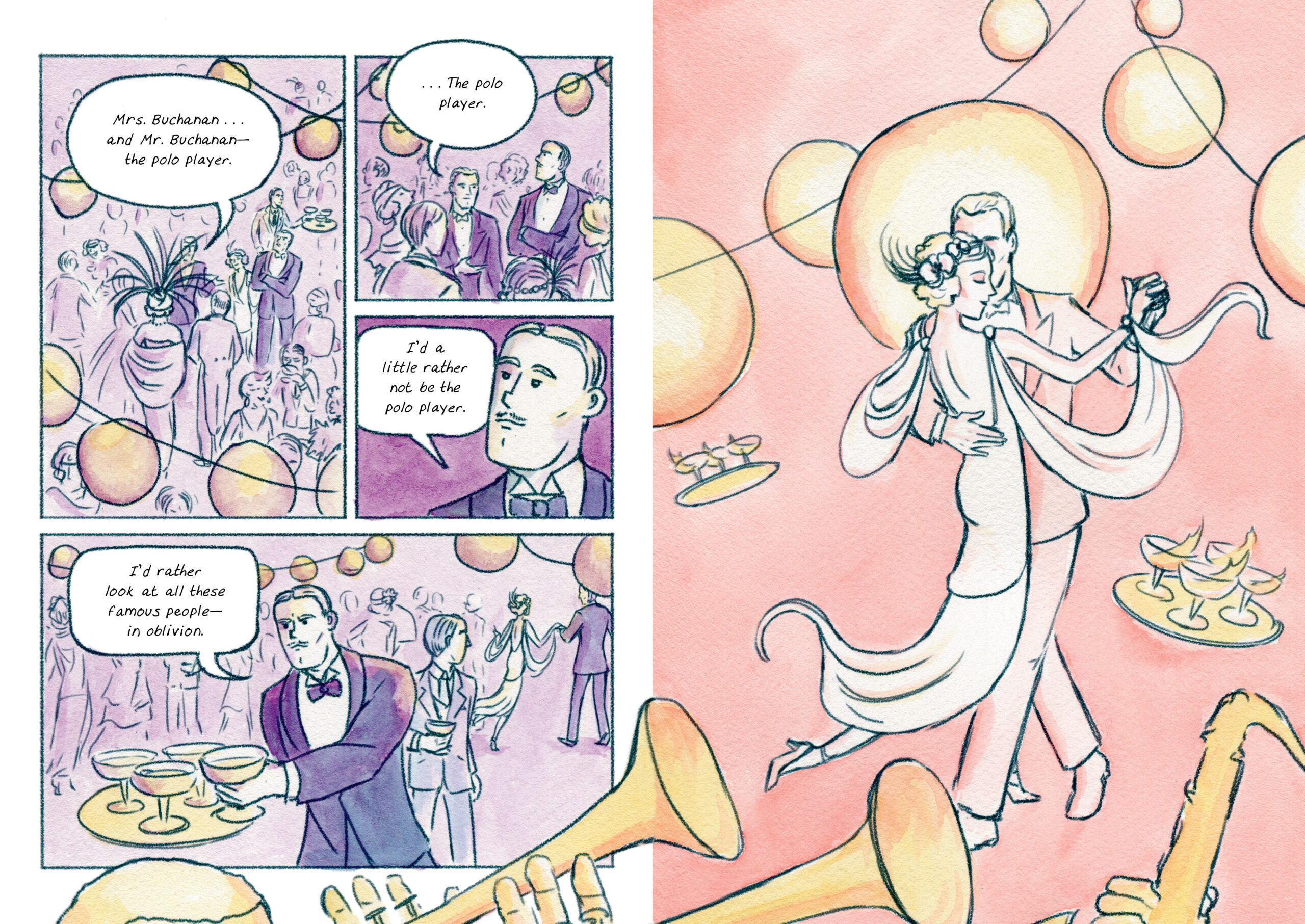
Or you could, just like Minneapolis-based artist K. Woodman-Maynard adapt the work into a beautiful graphic novel, pages of which you can glimpse here. Her version is all light and pastel watercolors, with a liberal use of the original text alongside more fantastic surreal imagery, making visual some of Fitzgerald’s word play. At 240 pages, there’s a lot of work here and, as if it needs repeating, no graphic novel is a substitute for the original, just…a jazz riff, if you were.
But Woodman-Maynard was one of many waiting for Gatsby to enter the public domain, which apart from Disney property, will happen to most recorded and written works over time. Many authors have been waiting for the chance to riff on the novel and its characters without worrying about a cease and desist letter. Already you can find The Gay Gatsby, B.A. Baker’s slash fiction reinterpretation of all the suppressed longing in the original novel; The Great Gatsby Undead, a zombie version; and Michael Farris Smith’s Nick, a prequel that follows Nick Carraway through World War I and out the other side. And there are plenty more to come.
Copyright law stipulates that any work after 95 years will enter the public domain. (Up until 1998, this used to be 75 years, but some lawyers talked to some congresscritters).
As of 2021, along with The Great Gatsby, the public domain gained:
Mrs. Dalloway – Virginia Woolf
In Our Time – Ernest Hemingway
The New Negro – Alain Locke (the first major compendium of Harlem Renaissance writers)
An American Tragedy – Theodore Dreiser (adapted into the 1951 film A Place in the Sun)
The Secret of Chimneys – Agatha Christie
Arrowsmith – Sinclair Lewis
Those Barren Leaves – Aldous Huxley
The Painted Veil – W. Somerset Maugham
Now, the thing about The Great Gatsby is that it is both loved by readers and hard to adapt into other mediums by its fans. It has been adapted five times for the screen (the Baz Luhrmann-Leonardo DiCaprio version is the most recent from 2013) and they have all dealt with the central paradox: Fitzgerald gives us so little about Gatsby. The author is intentionally hoping the reader to create this “great man” in our heads, and there he must stay. The novel is very much about the “idea” of a man, much like the idea of the “American Dream.” But film must cast somebody and Hollywood absolutely has to cast a star like Leonardo DiCaprio or Robert Redford. A graphic novel, however, does not have those concessions to the market. Woodman-Maynard’s version is not even the first graphic novel based on Fitzgerald’s book—-Scribner published a version adapted by Fred Fordham and illustrated by Aya Morton last year—-and it certainly will not be the last. Get ready for a bumper decade celebrating/critiquing the Roaring ‘20s, while we still figure out what to call our own era.
Related Content:
The Great Gatsby and Waiting for Godot: The Video Game Editions
The Wire Breaks Down The Great Gatsby, F. Scott Fitzgerald’s Classic Criticism of America (NSFW)
Ted Mills is a freelance writer on the arts who currently hosts the Notes from the Shed podcast and is the producer of KCRW’s Curious Coast. You can also follow him on Twitter at @tedmills, and/or watch his films here.
The Great Gatsby Is Now in the Public Domain and There’s a New Graphic Novel is a post from: Open Culture. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, and Google Plus, or get our Daily Email. And don't miss our big collections of Free Online Courses, Free Online Movies, Free eBooks, Free Audio Books, Free Foreign Language Lessons, and MOOCs.
from Open Culture https://ift.tt/3pwbrjE
via Ilumina
Comments
Post a Comment